- Improves QIVIVE & toxicity evaluations
- Influences pharmacokinetic properties
- Determines the effective concentration Cfree
- > 21.000 data records
- > 8.400 diverse compound structures
- taken from > 2.800 scientific publications
The database development started in 2005, it now contains:
Plasma Protein Binding Database
Drugs and toxic substances can be bound to proteins in plasma or blood, which reduces the free (effective) concentration of compounds in vivo. For toxicity evaluations and in drug discovery it is important to know to which extend a compound is bound to plasma proteins (PPB%):
Data records are comprehensively curated and annotated with more than 21 data fields describing the species, exp. conditions & methods (EQ, UF, UC, GF, albumin binding), compound concentration, etc.
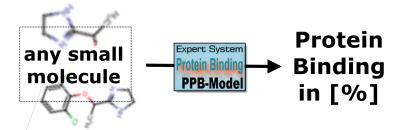
The expert system is now available for research projects and toxicological risk assessment. The AI-based technology evaluates the protein binding of any small molecule compound in human.
To use our prediction service or to obtain more information, please give us a call (+49 4921-993360) or send an email by clicking the button:

Reliable models to forecast plasma protein binding (PPB%) of substances have been created and show a high quality of prediction. We found a low Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and a high correlation between experimental and predicted PPB values based on a large and independent validation dataset.
An outstanding quality of prediction was achieved: Compared to conventional methods which forecast plasma protein binding by compound structure the error of prediction was reduced by half. The project results were presented at the BMBF-Statusseminar in Berlin.
The expert system to evaluate plasma protein binding of a compound in humans is now ready to use. Only the compound structure is needed. Contact us for further details (email).
|
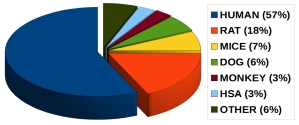
Plasma protein binding data from different species: |
|
|
|


|
© Copyright 2004-2021 PharmaInformatic Boomgaarden. All rights reserved. Site map Contact Terms of Use Imprint |

QIVIVE
Quantitative In Vitro to In Vivo Extrapolation
In order to correlate
IN VITRO results
with
IN VIVO observations, plasma protein binding
of a compound
is needed.
The effective
concentration
Cfree or Cunbound
can be largely different
from the nominal concentration
of compounds due to
plasma protein binding.