Analysing compound databases from external suppliers
Our customers buy external compounds from external suppliers to increase the size of their in-house database. One of our customers, concerned with the discovery of new antibacterials provided us with two databases, each consisting of 195.064 and 100.448 molecules. The client could not afford to buy all of the compounds, and we have been instructed to find the molecules with the highest MolScore-Antibiotics result.
We calculated the MolScore-Antibiotics of all molecules and ranked them. Our prediction on the first database gave the following results:
The database has 195.064 compounds.
More than 90% of the molecules in the database had a MolScore-Antibiotics result lower than 0,3 and were not suitable for the customer.
About 3.300 compounds (2%) had a MolScore-Antibiotics result higher than 0,8. From these, the customer chose some and examined their antibiotic activity.
Our prediction on the second database gave the following results:
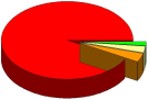
91%
2%
4%
3%
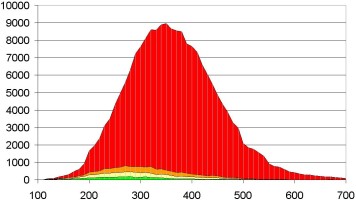
Number of molecules per row
Molecular weight
The database has 100.448 compounds.
More than 83% of the molecules in the database had a MolScore-Antibiotics result lower than 0,3 and were not suitable for the customer.
Less than 5.900 compounds (6%) had a MolScore-Antibiotics result higher than 0,8. From these, the customer chose some and examined their antibiotic activity.
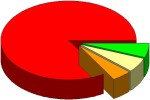
83%
6%
5%
6%
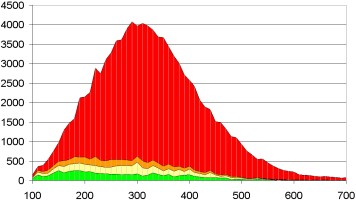
Number of molecules per row
Molecular weight
Given the cost per compound from external suppliers, the client saved a significant amount of money. Through focussing on the few selected compounds for his research programme, he saved time and resources.
MolScore-Antibiotics detects any type of antibiotics, regardless of mechanism of action or molecular weight. See further examples.
195.064 compounds
100.448 compounds

All
antibiotic
classes
can be identified
by
MolScore-
Antibiotics, regardless of mechanism of action or molecular weight.
See
further examples.
An expert system to calculate oral bioavailability in humans.


|
© Copyright 2004-2021 PharmaInformatic Boomgaarden. All rights reserved. Site map Contact Terms of Use Imprint |


