Detecting future drugs (antibiotics)
MolScores-Antibiotics is able to detect future antibiotics. The expert system has been validated with novel antibacterial substances, which are now in clinical development.

An expert system to identify suitable antibacterial candidates.
New Chemical Entities (NCE)
are recognised by MolScore- Antibiotics.

An expert system for finding
suitable
drug candidates.

An expert system to identify suitable antiviral candidates.
Antibiotic or not?
More than 95% have been assigned correctly. Analysis based on
5000 compounds (independent validation data).
Please be aware that drug status changes and the information provided here may be outdated.
For actual and comprehensive information about current drug status or clinical trials please check on the company’s home page.
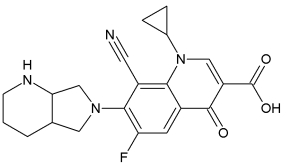
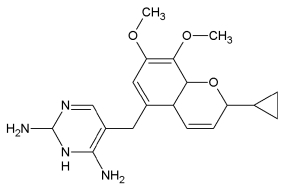
Iclaprim:
Iclaprim from Arpida Ltd. is a novel selective dihydrofolate inhibitor, which was developed by rational drug design. Injectable iclaprim has completed a Phase II clinical trial. In March 2005, Arpida received clearance from FDA to conduct Phase III clinical trials for injectable iclaprim in the USA. An oral formulation of iclaprim is in Phase I clinical trials. Arpida has completed first-in-man studies comparing oral and injectable iclaprim in healthy volunteers to determine absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion. Iclaprim demonstrated high absorption and extensive distribution in this study. In March 2006 Arpida Ltd. announced that it has received the recommendation from an independent Data and Safety Monitoring Board to continue the Phase III clinical trials for intravenous iclaprim for the indication complicated Skin and Skin Structure Infection.
Kohlhoff SA, Roblin PM, Reznik T, Hawser S, Islam K, Hammerschlag MR. In vitro activity of a novel diaminopyrimidine compound, iclaprim, against Chlamydia trachomatis and C. pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 May; 48(5):1885-6.
Schneider P, Hawser S, Islam K., Iclaprim, a novel diaminopyrimidine with potent activity on trimethoprim sensitive and resistant bacteria. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Dec 1;13(23):4217-21.
In January 2009, the US FDA issued a Complete Response Letter, stating they cannot approve the application for iclaprim in its current form and that additional clinical data are required to demonstrate efficacy in order to gain approval. Having undergone Phase III trials Iclaprim has been accepted as New Drug Application by the FDA for the treatment of complicated skin and soft-tissue infections.
Pradofloxacin (Bayer AG) was developed for use in animals, see Susanne Heinzl, Chemother. J. 2003; 12 : 21-20.
In May 2006 the European Medicines Agency adopted a negative opinion, recommending the refusal of the marketing authorisation for the medicinal product Veraflox (pradofloxacin). They concluded that the safety of pradofloxacin had not been conclusively proven. In April 2011 a marketing authorisation valid throughout the European Union was granted for Pradofloxacin (Tradename: Veraflox) to Bayer Animal Health GmbH.
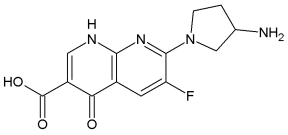
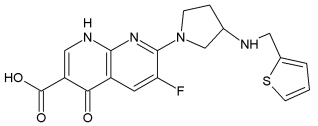
A-692345:
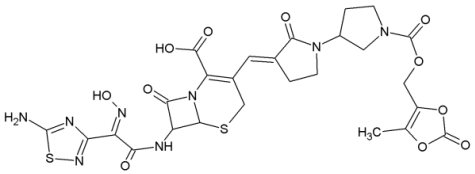
BAL 9141:
BAL5788 (Ceftobiprole, Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd) is the first of a new generation of anti-MRSA cephalosporins with good activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Ceftobiprole entered into phase III clinical trials in November 2004. BAL9141 is the active principle of prodrug BAL5788, which is water-soluble. In March 2006 Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd. announced positive results for its first comparative phase III trial with ceftobiprole.
Schmitt-Hoffmann A, Nyman L, Roos B, Schleimer M, Sauer J, Nashed N, Brown T, Man A, Weidekamm E. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of a novel broad-spectrum cephalosporin (BAL5788) in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Jul;48(7):2576-80.
Ceftobiprole medocaril for injection is the first approved broad-spectrum anti-MRSA antibiotic belonging to the cephalosporin class.
Ceftobiprole was approved in Canada in June 2008 (tradename: ZEFTERA) but the sale was discontinued in 2010. The European Marketing Authorization rejected a marketing authorisation application for ceftobiprole in June 2010. A European Marketing Authorization Application for ceftobiprole for the treatment of pneumonia in the hospital has been accepted for review in October 2012.
Peter J. Dandliker et al. from Abbott Laboratories, reported the discovery and characterisation of a novel ribosome inhibitor (NRI) class that exhibits selective and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. The chemical structure of the NRI class is related to antibacterial quinolones, but the differences in structure are sufficient to completely alter the biochemical and intracellular mechanisms of action. Some compounds in the NRI series appear to inhibit bacterial ribosomes by a new mechanism, because NRI-resistant strains are not cross-resistant to other ribosome inhibitors, such as macrolides, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, aminoglycosides, or oxazolidinones. The NRIs are a promising new antibacterial class with activity against all major drug-resistant respiratory pathogens.
Peter J. Dandliker, Steve D. Pratt, Angela M. Nilius, Candace Black-Schaefer, Xiaoan Ruan, Danli L. Towne, Richard F. Clark, Erika E. Englund, Rolf Wagner, Moshe Weitzberg, Linda E. Chovan, Robert K. Hickman, Melissa M. Daly, Stephan Kakavas, Ping Zhong, Zhensheng Cao, Caroline A. David, Xiaoling Xuei, Claude G. Lerner, Niru B. Soni, Mai Bui, Linus L. Shen, Yingna Cai, Philip J. Merta, Anne Y. C. Saiki, and Bruce A. Beutel Novel Antibacterial Class, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 12, 3831.
|
NCE |
Company |
Country |
|
Novexel (acquired by AstraZeneca) |
France |
|
|
Novexel (acquired by AstraZeneca) |
France |
|
|
Austria |
||
|
Austria |
||
|
Austria |
||
|
USA |
||
|
USA |
||
|
Switzerland |
||
|
Germany |
||
|
Switzerland |
||
|
Switzerland |
||
|
USA |
||
|
Canada |
||
|
USA |
||
|
USA |
In July 2005 Paratek Pharmaceuticals announced phase I trial of PTK0796, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic. PTK 0796 inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. PTK 0796 is an oral and intravenous antibiotic for treatment of life threatening infections such as complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) and moderate to severe community acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP), with activity against resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), multi-drug resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (MDRSP) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). In October 2009 Paratek Pharmaceuticals announced that it has entered into an exclusive worldwide collaborative development, manufacturing and commercialisation license agreement with Novartis for PTK 0796, a first-in-class aminomethylcycline (AMC) in Phase 3 clinical trials.
In December 2005 Theravance, Inc. announced that results with the investigational antibiotic telavancin (TD-6424), from a phase 2 clinical study in patients with complicated gram-positive skin and skin structure infections and from a phase I study in healthy volunteers, were presented at the 45th annual Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC) meeting in Washington D.C.
In September 2009 the U.S. FDA has approved Telavancin for the treatment of adult patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, both methicillin-resistant (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible (MSSA) strains.

An expert system for finding molecules with antibiotic activity.
Our
expert systems
are based on novel models and innovative methods in the field of drug design.
We use proprietary molecular descriptors and a huge amount of data and knowledge from literature to find relationships between molecular structures and biological activity.
The knowledge of our expert systems is used by our clients to filter large compound libraries.
Please be aware that drug status changes and the information provided here may be outdated.
For actual and comprehensive information about current drug status or clinical trials please check on the company’s home page.

Expert system
to estimate
oral bioavailability
in humans.
Below are some examples of substances which are currently in development by various companies. New chemical entities are recognised by MolScore-Antibiotics, regardless of substance-classes, mechanism of action or molecular weight.
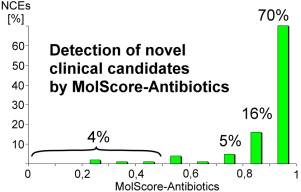
96% of clinical candidates have been correctly classified as antibacterial substances, which are suitable for further development into drugs.
As much as 70% of these molecules had a prediction result between 0,9 and 1,0. This validation demonstrates the excellent prediction capability of MolScore-Antibiotics to detect antibacterial clinical candidates.
AC98-6446 represents a novel class of glycopeptide antibiotics. It exhibits excellent in vitro activity against resistant gram-positive pathogens, which was also demonstrated in vivo in three different animal models of infection. It was selected for further study.
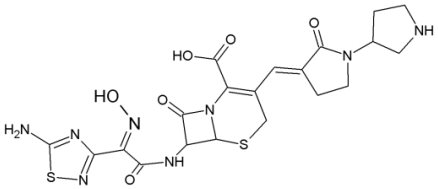
BC-1175 is a novel broad spectrum cephem-3-azomethine. It exhibited an excellent antimicrobial profile including various Enterobacteriaceae, E. faecalis, S. aureus and MRSA and was selected for further investigations.
BC-2901 is a broad-spectrum cephalosporin exhibited an excellent antimicrobial profile including various Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus faecalis, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. It was selected for further development.
BC-3781 interferes with bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the peptidyl transferase center of the ribosomal 50S subunit. This inhibition can implies a low probability of cross-resistance with other antimicrobials currently used for systemic treatment. BC-3781 has successfully finished a phase II clinical trial in patients with ABSSSI (see clinical trials.gov identifier NCT01119105). Medline-Link
The glycosylated polyketide defines a new antibacterial structural class. It shows strong antibacterial activity against Gram-positive pathogens like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE).
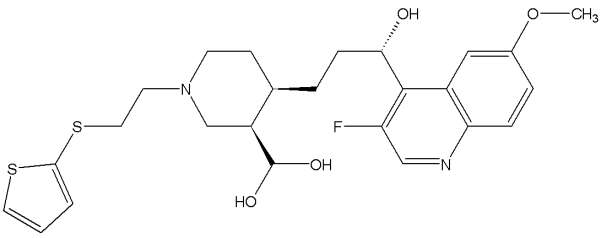
NXL101 is an inhibitor of bacterial topoisomerase which is highly active against gram positive pathogens. In June 2008 Novexel decided to discontinue the development of NXL101, because during clinical development NXL101 has prolonged the QT interval in healthy subjects.
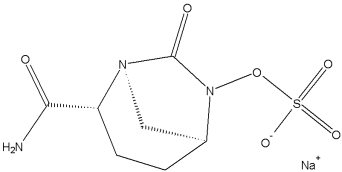
NXL-104 is a representative of a novel class of bridged bicyclico[3.2.1] diazabicyclo-octanones.
The compound is a potent inhibitor of a wide range of beta-lactamases.
It has demonstrated, in partnership with beta-lactam antibiotics, the potential to treat drug resistant gram-negative bacteria.
In March 2009 NXL104 has entered a second phase II clinical trial. In December 2009 Novexel was acquired by AstraZeneca. In December 2010, it entered a comparative phase II clinical trial in adult subjects with complicated urinary tract infections. In order to compare the effects of Ceftazidime/ Avibactam with Doripenem for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections including acute pyelonephritis, a phase III trial began in October 2012.

An expert system for finding molecules with antibiotic activity.
Our
expert systems
are based on novel models and innovative methods in the field of drug design.
We use proprietary molecular descriptors and a huge amount of data and knowledge from literature to find relationships between molecular structures and biological activity.
The knowledge of our expert systems is used by our clients to filter large compound libraries.
Please be aware that drug status changes and the information provided here may be outdated.
For actual and comprehensive information about current drug status or clinical trials please check on the company’s home page.

An expert system for finding molecules with antibiotic activity.
Our
expert systems
are based on novel models and innovative methods in the field of drug design.
We use proprietary molecular descriptors and a huge amount of data and knowledge from literature to find relationships between molecular structures and biological activity.
Further Links:
PACT-F
Drug design
Drug discovery
Drug development
Cheminformatics
ADME
Pharmacokinetics
Bioavailability
Computational chemistry
Molecular
modeling
Clinical trials
Preclinical
Research

Expert system
to estimate
oral bioavailability
in humans.


|
© Copyright 2004-2021 PharmaInformatic Boomgaarden. All rights reserved. Site map Contact Terms of Use Imprint |

